Prostatitis- a common disease in men of reproductive age and the elderly.
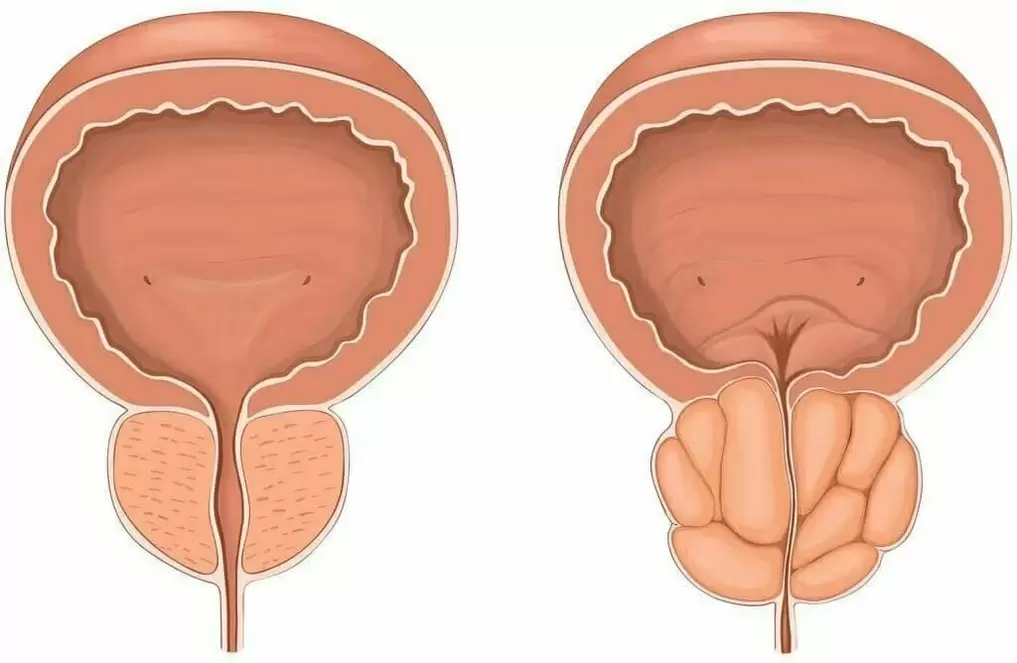
What is prostatitis? This is an inflammation of the prostate gland in men, this organ is also called the prostate. The prostate gland is very close to the neck of the bladder and is an important part of the male reproductive system. Inflammation of the prostate causes its enlargement, as a result of which the urinary tract is compressed and the process of emptying the bladder becomes difficult, and other unpleasant symptoms appear. Therefore, in case of inflammation of the prostate, it is not recommended to be inactive.
Symptoms and signs of prostatitis.
Usually men pay due attention to the manifestations of prostatitis quite late. The clinical picture of each case is individual, even if we are talking about one form of the disease. However, the first symptoms of prostatitis in men are roughly the same:
- Difficulty urinating. . . The urethra, which is compressed under the swollen prostate, does not urinate well. A feeling of incomplete emptying and a constant urge to urinate are also the first signs of prostatitis in men, and your symptoms will worsen in the future.
- Sexual disorders. . . These unpleasant signs of inflammation of the prostate appear in men mainly as a violation of the erection mechanism and a weakening of orgasm. Also, symptoms of inflammation of the prostate include premature ejaculation.
- Pain. . . Among the signs of inflammation of the prostate gland in men is pain when urinating and ejaculation, a characteristic symptom is also constant pain in the lower back.
- Nervous tension. . . Symptoms of inflammation of the prostate include increased nervousness in a man, as an enlarged prostate causes some discomfort.
Causes of prostatitis
Inflammation of the prostate gland occurs for various reasons:
- Poor blood circulation. . . Blood circulation can be affected due to physical inactivity (sedentary lifestyle and sedentary lifestyle); This is a very common cause of prostate inflammation in men. Also, the cause of a violation of the blood supply to the organs is a large weight, a trauma to the small pelvis, constant hypothermia.
- Infection. . . Infectious diseases also often cause prostatitis. The prostate gland is easily infected as a result of venereal and urological diseases, inflammatory processes in the rectum, and complications after infectious diseases (tonsillitis, pneumonia, tuberculosis).
- Immune deficiency. . . The weakening of the protective functions of the body due to past diseases, stresses, etc. , it often becomes the cause of prostatitis in men or the aggravation of an existing disease.
Types of prostatitis
Acute prostatitis develops rapidly with the rapid onset of characteristic symptoms. Chronic prostatitis often occurs with a gradual and almost imperceptible development of symptoms, it is typical for men over 55 years of age.
In addition, prostatitis is classified by origin:
- Bacterial.Most often it occurs at a young age, but among other types of disease, these cases are only 5-10%. Usually, acute and chronic bacterial prostatitis occurs due to the body's vulnerability to pathogenic flora.
- Infectious. . . Infectious prostatitis is caused not only by bacteria, but also by fungi, protozoa, which distinguish it from the bacterial variety. This type of disease can also present in chronic and acute forms. One of its characteristic varieties is chlamydial prostatitis.
- Purulent. . . Purulent prostatitis is one of the most serious types of infections, with purulent discharge and hyperthermia from the body. The course of the disease is acute, with the appearance of new symptoms at each stage.
- Calculation. . . Calculous prostatitis is a consequence of a long chronic form and is seen mainly in older men. This form of the disease is characterized by the appearance of stones in the prostate.
- Stagnant. . . Non-bacterial prostatitis, which is caused by insufficient blood supply to the tissues of the pelvic organs. Congestive prostatitis, as it is also called, is usually chronic. Of all the types, congestive prostatitis is the most common.
Why is prostatitis dangerous?
In any man, prostatitis without timely treatment quickly becomes chronic and has serious consequences for reproductive health and the general condition of the body. The most common complications of prostatitis include:
- Vesiculitis. . . Inflammation of the seminal vesicles is the first thing that makes chronic prostatitis dangerous for men. Vesiculitis can present without any symptoms or manifest itself by pain when urinating, after intercourse, as well as by the appearance of pus and blood in the semen.
- Posterior urethritis and colliculitis.. . . The danger of prostatitis lies in the development of posterior urethritis and concomitant colliculitis. Colliculitis is an inflammation of the seminal tubercle that allows the passage of sperm. One of the symptoms of colliculitis is the presence of blood in the semen.
- Prostate diseases. . . The consequences of prostatitis in men can be other more serious diseases of the prostate: abscesses, sclerosis, cysts and stones, adenoma, cancer. Such complications are treated much more difficult and prolonged than prostatitis, and the consequences of some of them are irreversible.
- Sexual dysfunction. . . The consequences of advanced inflammation of the prostate can be problems in the genital area, including erectile dysfunction. Although impotence resulting from prostatitis can be cured, it is often irreversible.
- Sterility. . . Since the reproductive system of the male body with inflammation of the prostate does not perform its functions well, infertility usually becomes a consequence of chronic prostatitis. It all starts with a deterioration in the quality of sperm and the patency of the vas deferens.
Prostatitis diagnosis
The diagnosis of prostatitis in men begins in the first minutes at a doctor's appointment, since the patient's complaints are an important part. In addition, to identify the disease and its characteristics, other types of diagnostics are used:
- Medical exam. . . During the medical examination, a digital-rectal examination is used, which is performed through the anus and allows you to identify the size, shape, surface condition and other characteristics of the prostate gland. Since it is extremely easy to diagnose prostatitis this way, this is actually the first and foremost method of confirming the diagnosis.
- Laboratory research. . . Prostatitis tests in men are used to study blood, urine, semen, and study of prostate secretions. One of the most effective methods is urinalysis for prostatitis (general, bacteriological, cytological). Also, with prostatitis, a general blood test is prescribed. In each case, the doctor determines what tests are done for prostatitis and if more in-depth research methods are needed.
- Non-invasive methods. . . These are ultrasound, X-ray diagnostic, and MRI.
Treatment of prostatitis
Self-medication for prostatitis is strongly discouraged. If a man does not know which doctor treats prostatitis, he can ask his therapist about it. But generally all patients know that a urologist specializes in treating prostatitis in men. It is also allowed to contact a therapist or surgeon, but only for the initial appointment.
Many patients are faced with a natural question: is it possible to cure prostatitis? It all depends on the form of the disease. But in any case, the diagnosis and treatment of inflammation of the prostate in men is necessary at the first warning signs, since chronic prostatitis will require more time and financial costs. Modern methods of treating prostatitis allow you to cope with any form and stage of the disease with minimal consequences for the body.
How long is prostatitis treated?
The amount of prostatitis that is treated and whether it can be cured without consequences depends on the complexity of the particular case. The sooner a man sees a specialist, the greater the chance of effective prostatitis treatment. The duration of treatment for prostatitis can be from 1 to 6 months, depending on the form of the disease. It is worth considering the time spent on diagnosis, which will also affect the duration of prostatitis treatment.
How and what to treat
There is no single treatment regimen for prostatitis, as this disease is very diverse and requires an individual approach. But regardless of the form, the following methods are used to treat prostatitis:
- Drug therapy. . . Antibiotics are used to treat acute and chronic prostatitis. This is a mandatory and essential part of the treatment of all types of prostate inflammation. In the acute course of the disease, the use of painkillers is allowed, since it usually takes a long time to treat prostatitis.
- Physiotherapy. . . The treatment regimen for prostatitis certainly involves physical therapy as a method of lightly massaging the prostate gland. In addition, herbal enemas and other procedures may be prescribed.
- Diet. . . Since it is difficult to cure chronic prostatitis or its acute form with a diseased intestine, a diet or dietary adjustment is prescribed.
- Physical exercises. . . This method of treating prostatitis is necessary to improve blood circulation in internal organs.
Prevention of prostatitis
To avoid prostatitis, both after a previous illness and in the absence of such experience, you will need to follow simple recommendations:
- Stable sex life. . . Sex life with a healthy partner will prevent not only sexually transmitted diseases, after which prostatitis often occurs, but also its stagnant form.
- Rejection of bad habits. . . An unhealthy lifestyle reduces the body's defenses, so it is best to avoid smoking, alcohol, and unhealthy foods.
- Sport activities. . . Exercise keeps the body in good shape and improves blood flow to the prostate gland, reducing the risk of prostatitis.
- Prostate massage. . . This is a secondary prevention measure of prostatitis in men for those who have already had the disease.
- Preparations for prophylaxis.. . . These are vitamin complexes that will help both to prevent prostatitis and to strengthen the immune system. Used as directed by a physician.
Prostatitis and conceiving a child
Whether it is possible to get pregnant with chronic prostatitis in a husband is a question that worries many families. It should be understood that the prostate is responsible for many of the most important functions associated with conception, therefore, prostatitis increases the likelihood of male infertility. The presence of infections and inflammation in the prostate affects the quality of ejaculation, and although it is possible to conceive a child with prostatitis, the chances of success are reduced.
Prostatitis and infertility are closely related, as with blocked vas deferens, a pregnancy may not occur after intercourse. The presence of purulent and bloody discharge in male sperm with prostatitis significantly affects their quality and reduces the probability of conception.
With prostatitis, you can conceive a child, but for the best result, you must first cure the disease and prevent possible infertility. Only after a man has cured prostatitis is it time to think about planning a pregnancy. For the treatment of prostatitis and planning the delivery, it is best to contact specialized centers that will definitely help to solve all the problems.